Composite Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Machinery With Collaborative Learning
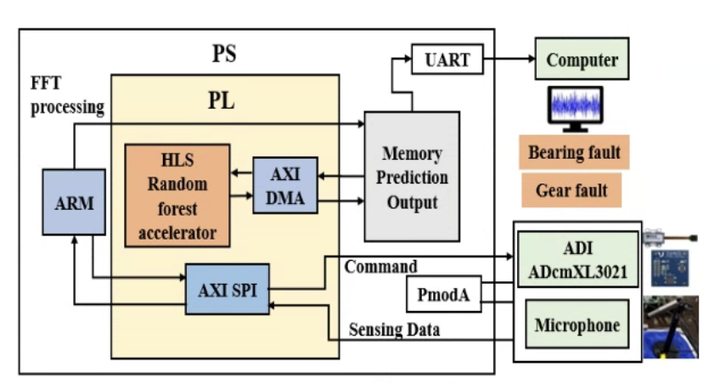 Image credit:
Unsplash
Image credit:
Unsplash
Abstract
Rotating machinery is a machine with a rotating component used for energy transformation, which is widely used in vehicle engines, power plants, manufacturing factories, etc. Because of the continuous rotation, the bearing and gear are subject to defects in the rotating machines, which damages the reliability of the machine. To provide a sustained normal working status, predictive maintenance (PdM) is usually applied to monitor the working health during the machine running by gathering different sensing data. However, highly diverse and massive sensing data increase the challenge of analyzing the fault signals in the machine. Besides, the situation with composite faults (i.e., faults that happen in different components in a machine) worsens the difficulty of diagnosing the target machine efficiently. To solve this problem, we propose a hierarchy collaborative learning method in this work. Different from conventional centralized learning to analyze heterogeneous sensing data, collaborative learning uses multiple sub-learning units to analyze the local homogeneous sensing data priorly. Then, perform fusion operation for each sub-learning unit obtained from homogeneous sensing data to predict the final composite fault diagnosis results. In this way, we can not only ensure the quality of the single fault diagnosis but also improve the accuracy of the composite fault diagnosis significantly. Compared with the centralized learning methods, the proposed collaborative learning method can achieve a 12% improvement in the accuracy of predicting the composite fault diagnosis.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code and math.